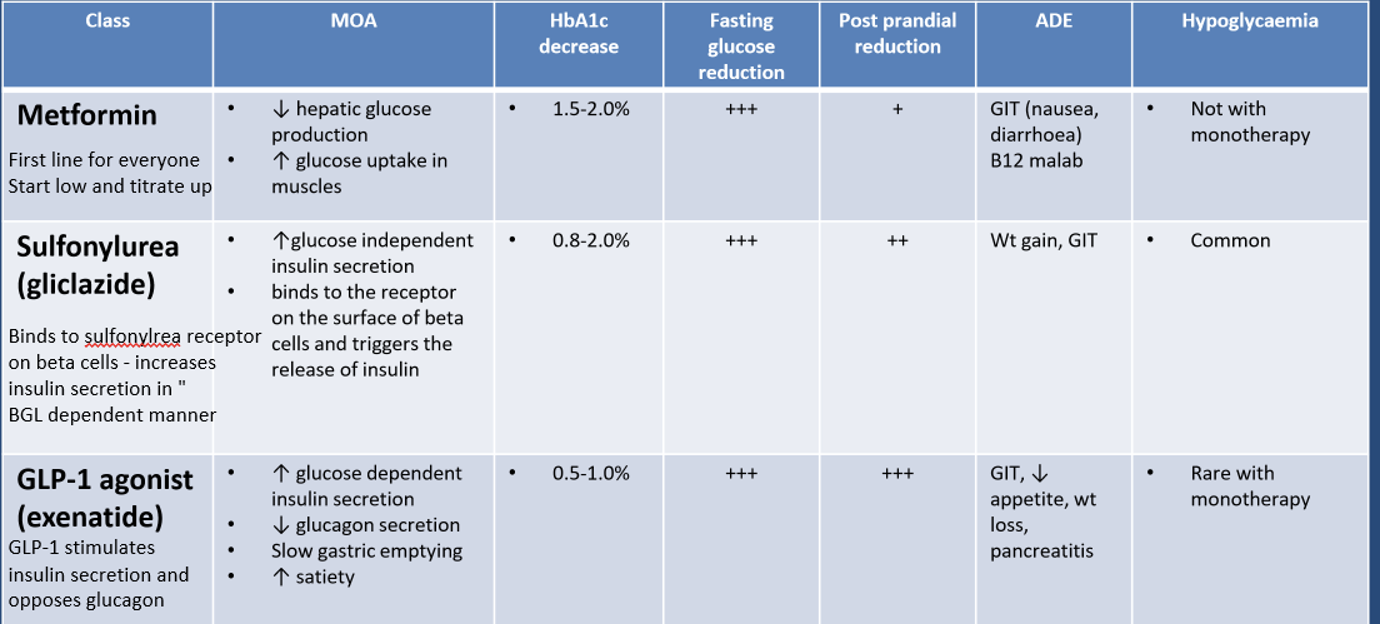
Types of drugs
1) Metformin
o MOA (mechanism of action)
- Decreases hepatic glucose production
- Increases glucose uptake into muscles
o 1.5-2% HbA1c decrease
o Large decrease in fasting glucose production
o Minor decrease in post-prandial glucose production
o Adverse drug effect (ADE) 부작용
GIT nausea and B12 malabsorption - rare
o As monotherapy - no hypoglycaemia risk
o FIRST LINE AGENT
- For nearly all patients
2) Sulfonylureas - Gliclazide
o MOA
- Binds to sulfonylurea receptor on pancreatic beta cells
· Increases insulin secretion INDEPENDENT of BGL
· Not suitable for use in complete beta-cell failure
o 0.8-2% HbA1c decrease
o Large fasting BGL reduction and moderate post-prandial BGL reduction
o ADE
- Weight gain
· Not suitable for obese patients
- GIT upset
o Hypoglycaemia is common
- May not be suitable in elderly patient with high risk of falls
3) GLP-1 agonist - Exenatide
o MOA
- GLP-1 analogue that binds to receptor
· Stimulates insulin secretion in a BGL dependent manner
· Decrease glucagon secretion
· Reduces hepatic glucose production
· Slows gastric emptying and increases satiation
o 0.5-1% HbA1c decrease
o Large decrease in both fasting and post-prandial glucose
o ADE
- GIT symptoms
- Decreased appetite and weight loss
· Useful in obese patients
- Pancreatitis
o Hypoglycaemia is rare with monotherapy
4) DPP-4 inhibitors - sitagliptin
o MOA
- DPP-4 inhibits GLP-1
- DPP-4 inhibitors block the DPP4 binding site on GLP-1
· Inhibit DPP4 from inactivating GLP-1
- Increases activity of GLP-1
· Increases glucose-dependent insulin secretion
· Decreases glucagon secretion
o 0.5-0.8% HbA1c reduction
o Minimal fasting glucose reduction
- Large post-prandial glucose reduction
o ADE
- Pancreatitis
o No hypoglycaemia with monotherapy
5) SGLT-2 inhibitors - empagliflozin
o MOA
- Binds and inhibits the Na/glucose transporter in PCT of nephron
o 0.7-1% decrease in HbA1c
o Moderate decrease in fasting and post-prandial glucose
o ADE
- Candidiasis
- UTIs
- Euglycemic DKA
o Low risk of hypoglycaemia
o Has cardiovascular disease benefits
- Preferentially given if patient has a history of CVDs
o Not useful in patients with renal failure as target is in the kidney

Type 1
· Insulin replacement
· Insulin regiments
o Basal-bolus
* Basal - approx 40% of daily dose
· Background - typically given at night
· Intermediate or long acting insulin
* Bolus - approx 60% of daily dose
· Used to cover carbohydrate intake with meals
· Use short of ultra-short acting insulin
*
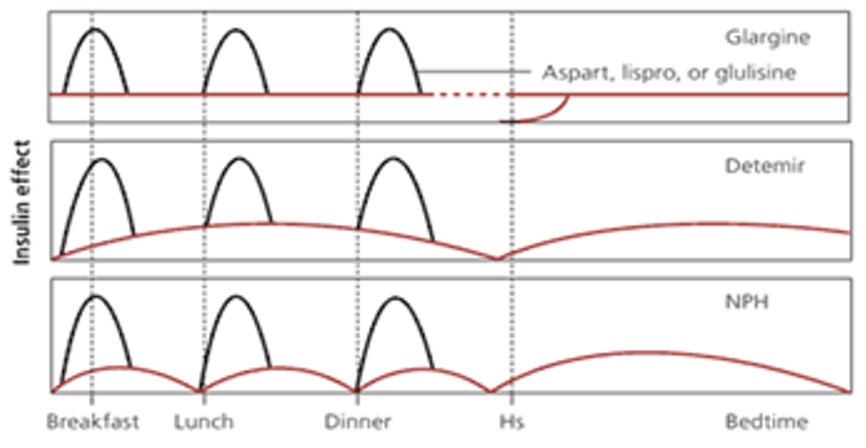
o Split-mixed
- Limited role in therapy of type 1
- Combines a short/ultra short acting with intermediate acting
- Generally used to decrease number of daily injections
· Difficult to tailor dose to specific BGL/patient
- Higher risk of hypoglycaemia due to dose stacking
o Continuous SC infusion
- Small programmable pump device outside the body
· Fine needle and cannula below the skin
- Delivers continuous steady rate of short or ultra-short acting basal insulin + bolus between meals
- Indications
· Failed other regiments
- Improved HbA1c and QOL
- Expensive

Type 2
· Lifestyle
o Exercise
o Dietary changes
o Weight loss
· Non-T2DM pharmacology
o Management of BP
- ACEI or ARB
o Management of dyslipidemia
- Statin therapy
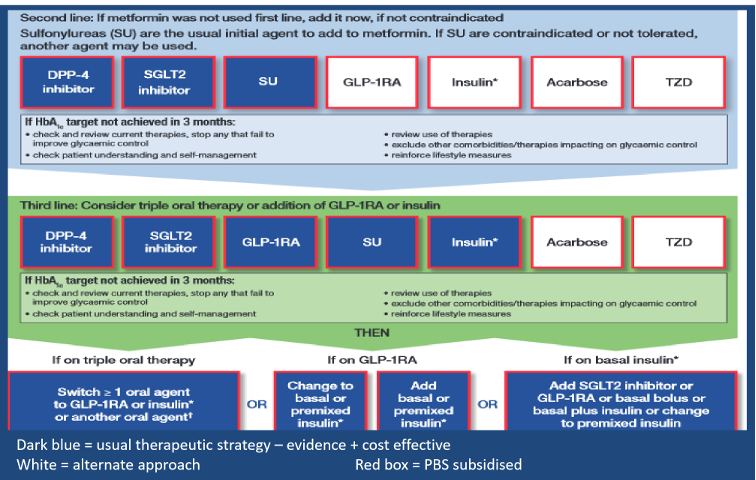
· T2DM pharmacology
o First line
- Metformin
o Second line
- Metformin + Addition depends on patient
· Heart failure or high CVD risk
· SGLT2 inhibitor - empagliflozin
· Renal failure
· CANNOT use SGLT-2 inhibitor
· Use DPP4-inhibitor - sitagliptin
· Very high post-prandial BGL
· Sulfonylurea - gliclazide
· Overweight patient
· CANNOT use sulfonylureas
o Third line
- Consider triple oral therapy of metformin + 2 others
- OR metformin + exenatide OR insulin
o Insulin
- Insulin can be added anywhere in the treatment algorithm
· Management of hyperglycaemia
o Many considerations to take with how stringent the management is

· Patient education
o Discuss at diagnosis that it is likely that the patient will require insulin
- Insulin doesn't indicate patient failure or therapeutic failure - indicates pancreatic failure
o Needle phobias
o Weight gains
'호주 의사 라이프:)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [호주 의사] 호주 간호사에서 호주 의사 되기 . 왜? (14) | 2024.01.01 |
|---|---|
| [호주 의사] 인턴쉽 마쳐간다 (0) | 2023.12.31 |
| 호주 의사 인턴 생활 - 나이트 근무 연속 7일 (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| 일반혈액검사 CBC test - 헤모글로빈 haemoglobin: 빈혈 (0) | 2023.02.19 |
| 하루 필수 영양소 Daily nutritional requirements (1) | 2023.01.26 |